Abstract
Objective:
Care burden threatens the physical, psychological, emotional, and functional health of caregivers. Caring for patients with delirium leads to stress, increased emotional load and workload in nurses. The strain of care for delirium index (SCDI) was developed to measure the subjective burden of nurse’s experience in the care of patients with delirium. The aim of this study is to examine the Turkish validity and reliability of the " The strain of care for delirium index ".
Materials and Methods:
This study was conducted in a methodological and cross-sectional type. The sample consisted of 102 nurses working in the intensive care unit for at least 6 months.
Results:
The goodness-fit indices obtained in the confirmatory factor analysis were at an acceptable level. In the explanatory factor analysis of the scale, factor loads were found to be between 0.343 and 0.865. Item-to- total correlation coefficients ranged from 0.298 to 0.627 and above 0.20 for each item.
Conclusion:
Reliability refers to consistency between independent measurements of the same thing. In this study, Cronbach's alpha coefficient and item-total correlations were used to measure reliability. In this study, the Cronbach's alpha coefficient was 0.89. Therefore, SCDI has been accepted as a highly reliable measurement tool. In the reliability analysis of the original index, the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was found to be 0.88. The Turkish version of the SCDI is a valid and reliable scale to evaluate the care difficulty of nurses caring for patients with delirium.
Keywords: Care burden, critical care, delirium, nursing, reliability and validity
Introduction
Delirium is an acute brain syndrome in which mental functions are generally reversible, with a sudden, fluctuating course in consciousness, perception, thought, sleep-wake cycle, which disrupts brain functions due to an organic cause, and the brain is widely affected in a short time (1, 2).
In a meta-analysis and systematic reviews conducted in different patient groups, it was stated that the incidence of delirium increased by up to 52% (3-5). In the literature, it is stated that delirium causes prolonged mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit (ICU), and hospital stay, increased mortality, and long-term cognitive impairment (6, 7). Patients may experience disturbing symptoms of psychosis, such as delusions, hallucinations, and altered mood. Patients with delirium tend to exhibit cognitive and behavioral fluctuations. Caregivers to patients with delirium have great difficulty managing these conditions (8). Studies have shown that delirium causes care difficulties for nurses (9, 10).
Caring for patients with delirium leads to stress and increased emotional load and workload in nurses (11). Care burden defines as a multidimensional response to the negative evaluation and perceived stress resulting from the care of the patient. Care burden threatens the physical, psychological, emotional, and functional health of caregivers (12, 13). In the literature, there are two studies evaluating the care difficulties of nurses who care for patients with delirium (10, 14). The strain of care for delirium index (SCDI) was developed to measure the subjective burden of nurses’ experience in the care of patients with delirium.
This study aimed to investigate the Turkish validity and reliability of the “The SCDI” developed to measure the subjective burden of nurses’ experience in the care of patients with delirium.
Materials and Methods
This study is a methodological and cross-sectional.
Study Sample
We used the matched sampling method in sample selection. It is recommended that the sample size be 5-10 times the number of items in the scale (15-17). Therefore, the sample size was planned to at least 100 intensive care nurses. The data were collected from the nurses who worked in the ICU of the training and research hospital for at least 6 months between March and May 2022 using a questionnaire collection method. A sample of 102 nurses who agreed to participate in the study.
Data Collection Tools
We collected data with the “introductory information form” and “SCDI”.
a. Introductory Information Form: This form includes the descriptive characteristics of nurses, such as gender, age, and working years. This form, developed by the researchers in line with the literature, consists of 8 questions.
b. SCDI: This scale was developed by Milisen et al.(18) The aim of this scale was to determine the difficulties experienced by nurses when providing care to patients with delirium. The scale comprises 20 items and is a four-point Likert scale. The scale consists of 4 sub-dimensions as “hypoalert behavior, fluctuating course and psycho-neurotic behavior, and hyperactive/hyperallert behavior”. The total score ranged from 20 to 80, with higher scores indicating greater difficulty in coping with delirium. The four-factor index explains 61.51% of the total variance and the internal consistency Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient is 0.88 (18).
Data Collection
We applied an introductory information form and an adapted scale to the nurses participating in the study. We applied the scale again after 6 weeks to evaluate its invariance. It took 1 min to answer the scale.
Statistical Analysis
Data Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 22.0 (SPSS, Inc. Chicago, IL, USA) and AMOS version 21. The content validity of the scale was examined with the Polit and Beck Content Validity Index by obtaining expert opinions.(19) Construct validity of the scale; analyzed by exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) (16, 20). In the reliability of the scale, item-total correlations were determined, and the internal consistency of the scale and its subdimensions was examined with the Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient (16, 21, 22).
Test-retest measurement results showed a normal distribution; the difference between the mean scores obtained from the two measurement results, invariance vs. time, was examined with the “t-test independent groups”. The Hotelling T2 test was used to evaluate whether the participants’ responses to the scale items were equal (Figure 1).
Ethical Approval
Ethics committee approval was obtained from the Izmir Katip Celebi University non-interventional clinical research ethics committee (decision number: 0399 and decision date: 21.09.2021), and written institutional permission was obtained from Atatürk Training and Research Hospital. Nurses working in the ICU were informed about the purpose and methods of the study, and verbal and written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Results
Characteristics of the Participants
The mean age of nurses was found to be 26.69±4.48 years; moreover, 78.4% were female, and 70.6% had undergraduate education. The nurses participating in the research had been working as nurses for a minimum of 6 months and a maximum of 22 years and have been working in the ICU for at least 6 months and a maximum of 16 years (Table 1). Of the participants, 75.5% stated that they received education on delirium.
| Table 1. The descriptive characteristics of intensive care nurses (n=102) | ||
|
|
± SD |
Range |
|
Gender |
N (102) |
% |
|
Woman |
80 |
78.4 |
|
Male |
22 |
21.6 |
|
Educational Status |
||
|
High school |
14 |
13.7 |
|
Associate degree |
9 |
8.8 |
|
License |
72 |
70.6 |
|
Graduate |
7 |
6.9 |
|
ICU |
||
|
Cardiovascular surgery |
26 |
25.5 |
|
Anesthesia and reanimation in the ICU |
33 |
32.4 |
|
Neurosurgery ICU |
10 |
9.8 |
|
General surgery ICU |
12 |
11.8 |
|
Neurology ICU |
5 |
4.9 |
|
Internal medicine ICU |
10 |
9.8 |
|
Coronary ICU |
6 |
5.9 |
|
Age |
26.69±4.48a |
22-43 |
|
Professional working year |
3.86±4.04a |
6 months-22 years |
|
Years working in an ICU |
2.98±3.40a |
6 months-16 years |
| aValues given are mean ± SD, ICU: intensive care unit, SD: standard deviation | ||
Validity analysis
1.Examination of Content-Language Validity
Language Validity
First, two native speakers translated the scale from English to Turkish to ensure the language validity of the “SCDI”. Second, two experts who were fluent in both the Turkish and English languages and cultures and did not see the English version of the original scale translated the scale from Turkish to English. Third, the English-Turkish and Turkish-English translations were checked, and they were found to be similar. Thus, a Turkish version of the scale was created.
Content Validity
To analyze the content validity, eight specialists, namely, physicians, nurses, and faculty members in the field of cardiovascular surgery and psychiatry, were asked to provide their opinions on the applicability and comprehensibility of the scale items translated into Turkish. The experts evaluated each item on a scale for content validity by scoring between 1 and 4 (1: The item is not suitable, 2: The item should be seriously reviewed, 3: The item should be reviewed, 4: Appropriate).
Scores were given by the experts to the items of the “SCDI” were analyzed using the Polit and Beck Content Validity Index. The content validity index was calculated for both the items and scales. The Content Validity Index of the scale: 1 and Item Content Validity Index: 1.
It was determined that there was consensus among the experts. The researchers made necessary corrections to the scale items according to the experts’ suggestions. The scale was then evaluated statistically without removing the items.
Pilot Application
After determining the language and content validity of the scale, a pilot application was conducted. This study was conducted with 20 intensive care nurses, who had the characteristics of the sample and 10% of the sample number (23). Data from the pilot application were excluded from the analysis of this study. In line with the suggestions, the root of the question was changed from “…how is it for you to take care of patients?” to “…how do you deal with patients?” Additionally, the 12th question was edited as “How do you deal with patients who go back and forth between conscious and unconscious periods?” After these revisions, the final scale version was applied to the sample group.
2. Construct Validity
EFA and CFA were performed to assess the construct validity of the scale.
EFA: EFA was conducted to determine the construct validity of the “SCDI” and to determine the factor structure. Therefore, the direct oblivion method, which is an oblique rotation method, was used because there was a relationship between the principal components and factors (24). Sample adequacy was evaluated with Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) value in EFA. The KMO value was 0.831, Bartlett’s Test χ2 (190) =943.577 and p<0.05 (significant). The SCDI, which consists of 20 items and a structure with 4 sub-dimensions (factors), explained 59.84% of the total variance.
The factor loads of the scale items were between 0.343 and 0.865 (Table 2).
| Table 2. Factor loads of scale items | |
|
Scale items |
Factor loadings |
|
1. How should you manage patients who are withdrawn or who are unusually quiet? |
0.606 |
|
2. How do you deal with apathetic, disinterested, or unmotivated patients? |
0.750 |
|
3. How should you manage patients with reduced motor activity? |
0.636 |
|
4. How do you manage patients who lack knowledge or understanding of their disease/condition? |
0.343 |
|
5. How should you deal with patients who have difficulty concentrating and are easily distracted? |
0.589 |
|
6. How do you manage patients who speak slowly or hesitantly? |
0.622 |
|
7. How should you deal with patients who make little eye contact? |
0.573 |
|
8. How do you deal with patients who call someone they know by a different name? |
0.865 |
|
9. How do you deal with patients who are talking to people who are not actually present? |
0.860 |
|
10. How do you manage patients who engage in repetitive behaviors? |
0.679 |
|
11. How should you deal with patients with inconsistent speech? |
0.640 |
|
12. How do you deal with patients who go back and forth between the conscious and unconscious periods? |
0.430 |
|
13. How should you deal with patients whose sleep/wake cycles are disrupted? |
0.597 |
|
14. How do you deal with restless or agitated patients? |
-0.633 |
|
15. How do you deal with patients making noise or shouting? |
-0.788 |
|
16. How do you manage patients who are irritable? |
-0.805 |
|
17. How should you manage patients with increased motor activity? |
0.504 |
|
18. How do you deal with uncooperative or difficult-to-manage patients? |
-0.631 |
|
19. How do you deal with patients trying to get out of bed inappropriately? |
-0.842 |
|
20. How do you deal with patients pulling tubes, dressings, and catheters, etc.? |
-0.801 |
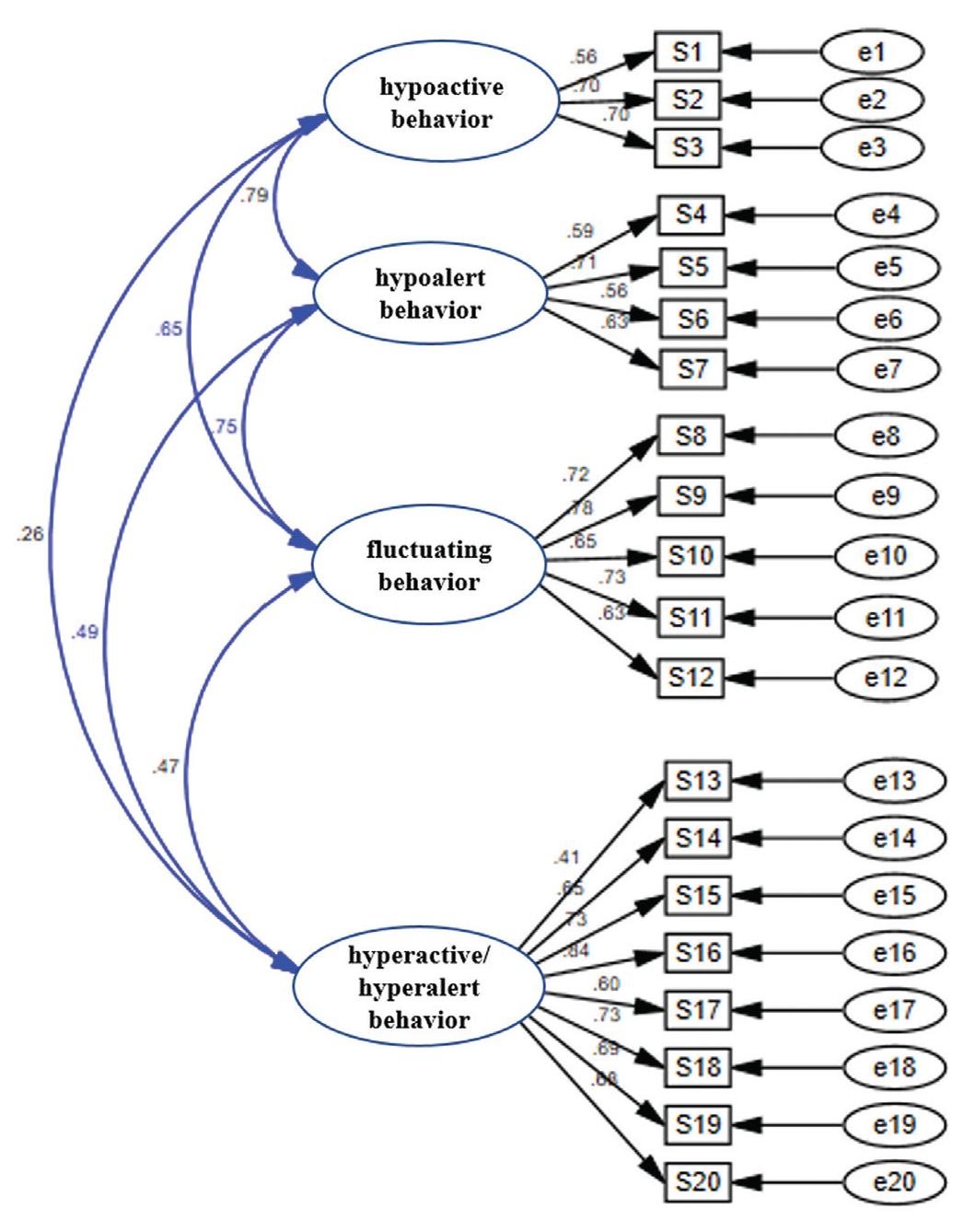
CFA: CFA was performed for the construct validity of the scale. CFA, the results of the fit statistics, and the modification index were examined without making any limitations on the model or adding new connections (Figure 2).
[(χ2(degree of freedom (df):164, n=102) =313.223, p=0.000, Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA)=0.095, Goodness of Fit Index (GFI)=0.775, Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index (AGFI)=0.711, Comparative Fit Index (CFI)=0.820, χ2/df=1.91] of the scale were obtained. p=0.000 was found (Table 3).
| Table 3. Examination of CFA compliance with the delirium difficulty-to-care scale | ||
|
DFA model fit indices |
Expected values |
SCDI |
|
Minimum fit function chi-square ( χ2 ) |
χ2/df <5 |
1.91 |
|
Degree of freedom (df) |
||
|
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) |
<0.08 |
0.095 |
|
Root Mean Square Residual (RMR) |
<0.08 |
0.045 |
|
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) |
>0.90 |
0.82 |
|
Goodness of Fit Index (GFI) |
>0.90 |
0.775 |
|
Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index (AGFI) |
>0.90 |
0.711 |
| CFA: Confirmatory factor analysis, SCDI: strain of care for delirium index, DFA: Detrended Fluctuation Analysis | ||
3. Reliability
1. Internal consistency
Cronbach’s alpha coefficient
SCDI (Cronbach’s alpha coefficient) was found to be α=0.892. Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for hypoactive, hypoalert, fluctuating course, and psycho-neurotic and hyperactive/hyperalert behavior subdimensions 0.675, 0.711, 0.828, and 0.863 were found, respectively (Table 4).
| Table 4. Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient and subdimension analysis results of the delirium difficulty of care scale and its subdimensions | |||||||
|
SCDI and its subdimensions |
± SD |
SE |
median |
min. |
max. |
r |
α |
|
1. Subdimension: Hypoactive behavior |
7.36±1.58 |
0.15 |
7.00 |
3 |
11 |
2.511 |
0.675 |
|
2. Sub-dimension: hypoalert behavior |
9.77±1.91 |
0.18 |
10.00 |
4 |
14 |
3.662 |
0.711 |
|
3. Subdimension: fluctuating course and psycho -neurotic behavior |
13.92±2.73 |
0.27 |
14.00 |
7 |
20 |
7.499 |
0.828 |
|
4. Subdimension: hyperactive/hyperalert behavior |
24.45±4.03 |
0.39 |
24.00 |
9 |
32 |
16.290 |
0.863 |
|
SCDI total |
55.50±7.94 |
0.78 |
56.00 |
35 |
75 |
63.064 |
0.892 |
| SCDI: Strain of care for delirium index, SD: standard deviation | |||||||
The mean SCDI score was 55.50±7.94 and the scale sub-dimension mean score was 7.36±1.58, 9.77±1.91, 13.92±2.73, and 24.45±4.03, respectively (Table 4).
Item-to-total score analysis
The item-to-total score correlation values of SCDI were between 0.298 and 0.627 and above 0.20 for each item. The item-total score correlation coefficients of the subdimensions were between 0.353 and 0.788.
2. Invariance analysis
Test-retest reliability coefficient (Test-retest reliability coefficient): SCDI was administered to 102 nurses working in the ICU twice, with an interval of 6 weeks. It was determined that there was no statistically significant difference between the two measurement results. (p=0.526) (p>0.05) (Table 5).
| Table 5. Test-retest mean scores of SCDI and its subdimensions | ||||||
|
|
Average score |
Analysis Results |
||||
|
Scale and subdimensions |
Test (n=102) ± SD |
Retest (n=102) ± SD |
t |
pb |
r |
pc |
|
SCDI |
55.50±7.94a |
55.59±8.06a |
-0.636 |
0.526 |
0.985 |
0.000 |
|
1. Subdimension: Hypoactive behavior |
7.36±1.58 |
7.34±1.58 |
0.533 |
0.595 |
0.972 |
0.000 |
|
2. Sub-dimension: hypoalert behavior |
9.77±1.91 |
9.73±1.90 |
0.815 |
0.417 |
0.968 |
0.000 |
|
3. Subdimension: fluctuating course and psycho -neurotic behavior |
13.92±2.73 |
13.91±2.70 |
0.155 |
0.877 |
0.973 |
0.000 |
|
4. Subdimension: hyperactive/hyperalert behavior |
24.45±4.03 |
24.60±4.13 |
-1,665 |
0.990 |
0.973 |
0.000 |
|
Total |
55.50±7.94 |
55.59±8.06 |
-0.636 |
0.526 |
0.985 |
0.000 |
| a Values are expressed as mean ± SD, b p >0.05, c p <0.001, SD: standard deviation, SCDI: strain of care for delirium index | ||||||
The test-retest total score average correlation coefficient of the scale was 0.985, and the subscale-total score correlation coefficients were 0.972, 0.968, 0.973, and 0.973, respectively, and were significant (p=0.000). In the first and second applications, a positive, very strong, and significant relationship was found between the scale and the subdimension total scores (Table 5).
3. Response Bias
Scale Response bias; The Hotelling T2 test was used to evaluate whether the participants responded to the scale items in line with the researcher’s expectations. Hotelling T2 =234.579 p=0.000, the scale did not have a response bias.
Discussion
Linguistic validity: First, two native speakers of Turkish translated the SCDI from English into Turkish to test the linguistic validity of the SCDI. Second, English by two experts, who were fluent in both Turkish and English languages and cultures but did not see the English version of the original scale, translated it back to English to test whether the Turkish version met the same meaning. In the third stage, the English-Turkish and Turkish-English translations were checked and found to be similar, and the Turkish form of the scale was created. Health professionals familiar with the terminology of the translated scale and who have experience in interviewing and data collection should be involved in the translation process. Translators should also consider the cultural, psychological, and grammatical differences between languages. In the initial and back translation, the emphasis should be on conceptual and cultural equivalence rather than linguistic equivalence (25). The back translation was compared with the original SCDI by the authors of this article, and no changes were made to the Turkish version as it was found to be compatible with the original scale. The language validity criterion of the scale is in line with the literature.
Content validity: Content validity is the extent to which the scale items of the construct to be measured represent the construct to be measured (26, 27). For this, the applicability and comprehensibility of the scale items translated into Turkish depend on expert evaluations, and choosing the right number of experts is very important (28). It is recommended to obtain expert opinion on content validity from at least three and at most 10 experts (19). So, expert opinion was obtained from 8 specialist who are experts in delirium and intensive care. The experts’ scores for the items of the SCDI were analyzed using the Polit and Beck Content Validity Index. For content validity, the Scale Content Validity Index: One and the Item Content Validity Index: 1. If an expert opinion is obtained from 6-10 people, it is recommended that the item and scale content validity index be 0.80 and above. It was determined that there was consensus among the experts (23). The researchers made necessary corrections to the scale items according to the suggestions of the experts. The pilot study was conducted with 20 intensive care nurses, who had the characteristics of the sample and 10% of the sample number (23). In the pilot study, participants were asked to read the question aloud and give a brief explanation about the meaning of each item. If an item is not easily understood, the respondent's opinion should be sought regarding how the question could be expressed in another way. In this way, it should be ensured that the substance is understood in the same way by every individual (25). According to the suggestions of the pilot study participants, we changed the roots of the questions and edited the 12th question.
Construct validity: EFA and CFA
In EFA, the researcher attempts to reveal the structure between variables, while CFA is suitable for situations where there are hypotheses about the structure in question based on pre-established or previous research and researchers are interested in testing them. The Bartlett test is used to determine whether the correlation coefficients are significant in EFA (29). The KMO was found to be 0.831, which indicates that the sample size was “perfect” for factor analysis. Also, Bartlett’s Test χ2(df:190) =943.577 and p<0.05 (significant), indicating that the correlation between items was large enough for EFA (17).
In the validity analysis of the scale, the total correlation coefficient was 0.88%. The factor loads of the scale items ranged from 0.343 to 0.865. It is recommended that the factor loads of the items be at least 0.32 (20). Factor loadings explaining the relationship between the factors show that the items are frequently highly correlated (Table 2). It was used to determine the degree of conformity of the subdimensions determined using EFA to the subdimensions created with the help of the hypothesis. It also determines the extent to which the scale items are represented by the determined factors Aytac and Öngen. (30). [(χ2(df:164, n=102) =313.223, p=0.000, RMSEA=0.095, GFI=0.775, AGFI=0.711, CFI=0.820, χ2/df:1.91] of the scale were obtained (Table 4). p=0.000 was found.
To achieve harmony between the matrices, the p value should be meaningless. The sample size greatly affects the p-value of the χ2 statistic and, therefore, results in the rejection of the model unless there are countless samples (31-33). In other words, the χ2 value is generally significant in practice. Therefore, the value obtained by dividing χ2 by the df can be considered (31). If χ2/df is 5 or less, it indicates that the model has an acceptable goodness of fit (31, 32). Our χ2/df value was 1.91 and has a good goodness of fit.
The RMSEA is the square root of the approximate means. It takes values between 0 and 1. If the RMSEA value is less than 0.05, it indicates a perfect fit; conversely, a value less than 0.08 indicates an acceptable fit. If the values are between 0.08 and 0.10, they show moderate agreement, while values below 0.10 are not considered acceptable (31, 32, 34, 35). RMSEA=0.095 and shows moderate agreement. As the Root Mean Square Residual (RMR) value approaches zero, the tested model shows better goodness of fit (31, 32, 34).
RMR=0.045, the model shows better goodness of fit. CFI gives the difference of the model established from the absence model (null), assuming that there is no relationship between the variables. This is a model that predicts that there is no relationship between the variables. The value of varies between 0 and 1. As the value approaches 1, it is concluded that the degree of goodness of fit increases, and simultaneously, the model with high value CFI exhibits a strong fit (31-34). CFI=0.82, goodness of fit was not as good as expected.
GFI is a goodness-of-fit index that indicates the extent to which the covariance matrix in the sample is measured by the model. The larger the sample size, the higher the GFI value. Although its general value is between 0 and 1, a GFI exceeding 0.90 is considered a good model indicator (32, 36). GFI=0.775, goodness of fit was not as good as expected.
The AGFI is the adjusted goodness-of-fit index. This index compensates for the deficiency in the GFI test in high sample volumes. Its value ranges from 0 to 1 and must be above 0.90 (31, 32, 34, 36). AGFI=0.711, and the goodness of fit was not as good as expected.
According to the Detrended Fluctuation Analysis result, χ2/df was found to have a good and moderate goodness of fit according to the RMSEA and RMR values. However, the goodness of fit of the CFI, GFI, and AGFI values was not as good as expected.
Reliability: Reliability refers to the consistency between independent measurements of the same thing. In this study, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient and item-total correlations were used to measure reliability (23). In this study, the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was 0.89. Therefore, SCDI has been accepted as a highly reliable measurement tool (21, 22). In the reliability analysis of the original index, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was found to be 0.88 (18).
Test-retest reliability is the power of a measurement tool to provide consistent results from application to application and to show invariance over time (37). Test-retest reliability is usually estimated by calculating the (38).
The test-retest total score average correlation coefficient of the scale was 0.985, and the subscale-total-score correlation coefficients were 0.972, 0.968, 0.973, and 0.973, respectively, and were significant (p=0.000) (Table 5). A very strong correlation between the two measurement values indicates greater temporal stability or test-retest reliability (38). The first and second application scale total and sub-dimension total point between a positive direction, very strong and significant a relationship to be this shows that the scale has an invariance feature against time and is consistent.
The reliability and validity studies of the scale were conducted only with intensive care nurses.
Conclusions
The SCDI is a valid and reliable tool for examining the burden of care in intensive care nurses caring for patients with delirium. In line with the data obtained from this scale, it is thought that it will help develop research directions to reduce or prevent the difficulty of nurses providing care to patients with delirium. The effectiveness of the interventions planned to reduce the burden of nurses in the care of these patients can be evaluated using this scale. The quality of patient care is expected to increase when the care burden of the nurses caring for patients with delirium is reduced.
Ethics
Ethics Committee Approval: Ethics committee approval was obtained from the İzmir Katip Celebi University non-interventional clinical research ethics committee (decision number: 0399 and decision date: 21.09.2021), and written institutional permission was obtained from Atatürk Training and Research Hospital.
Informed Consent: Nurses were informed about the study, and written informed consent was obtained.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the intensive care nurses who agreed to participate in this study. The authors thank specialist nurses, psychiatrists, associate professors, and assistant professors who contributed to the study with their language translation and expert opinions for their contributions to the study.
Footnotes
Authorship Contributions
Surgical and Medical Practices: M.U, Concept: M.U, A.D.E., Design: M.U, A.D.E., Data Collection and Process: M.U., Analysis or Interpretation: M.U, A.D.E., Literature Search: M.U, A.D.E., Writing: M.U, A.D.E.
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Financial Disclosure: The authors declare that they received no financial support for this study.
Ethics
Acknowledgements
Authorship Contributions
References
- Çam O, Engin E. Ruh Hastalıkları Hemşireliği Bakım Sanatı. 1. ed. İstanbul: İstanbul Tıp Kitabevi; 2014.
- Fan Y, Guo Y, Li Q, Zhu X. A review: nursing of intensive care unit delirium. Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 2012;44:307-16.
- Jung P, Puts M, Frankel N, Syed AT, Alam Z, Yeung L, et al. Delirium incidence, risk factors, and treatments in older adults receiving chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Geriatric Oncology. 2021;12(3):352-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgo.2020.08.011 .
- Lee A, Mu J, Joynt G, Chiu C, Lai V, Gin T, et al. Risk prediction models for delirium in the intensive care unit after cardiac surgery: a systematic review and independent external validation. BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia. 2017;118(3):391-9.
- Shao S-C, Lai C-C, Chen Y-H, Chen Y-C, Hung M-J, Liao S-C. Prevalence, incidence and mortality of delirium in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age and ageing. 2021;50(5):1445-53. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afab103 .
- Kang J, Lee M, Ko H, Kim S, Yun S, Jeong Y, et al. Effect of nonpharmacological interventions for the prevention of delirium in the intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of critical care. 2018;48:372-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.09.032 .
- Tilouche N, Hassen MF, Ali HBS, Jaoued O, Gharbi R, El Atrous SS. Delirium in the intensive care unit: incidence, risk factors, and impact on outcome. Indian journal of critical care medicine: peer-reviewed, official publication of Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine. 2018;22(3):144.
- Wilson JE, Mart MF, Cunningham C, Shehabi Y, Girard TD, MacLullich AM, et al. Delirium. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2020;6(1):1-26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00223-4.
- Detroyer E, Dobbels F, Debonnaire D, Irving K, Teodorczuk A, Fick DM, et al. The effect of an interactive delirium e-learning tool on healthcare workers’ delirium recognition, knowledge and strain in caring for delirious patients: a pilot pre-test/post-test study. BMC medical education. 2016;16(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-016-0537-0 .
- Tan H, Zhou L, Wu S, Dong Q, Yang L, Xu J, et al. Subjective strain of care experienced by pulmonary and critical care medical nurses when caring for patients with delirium: a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Services Research. 2021;21(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-06860-z .
- Sanson G, Khlopenyuk Y, Milocco S, Sartori M, Dreas L, Fabiani A. Delirium after cardiac surgery. Incidence, phenotypes, predisposing and precipitating risk factors, and effects. Heart & Lung. 2018;47(4):408-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrtlng.2018.04.005 .
- Işıl Ö, Yaşlı ON. demanslı bireye bakım verenlerde bakım yükü ve yaklaşımlar. T3 rkiye Klinikleri Dergisi. 2016;2(1):74-80.
- Liu Z, Heffernan C, Tan J. Caregiver burden: A concept analysis. International journal of nursing sciences. 2020;7(4):438-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2020.07.012.
- Schmitt EM, Gallagher J, Albuquerque A, Tabloski P, Lee HJ, Gleason L, et al. Perspectives on the delirium experience and its burden: common themes among older patients, their family caregivers, and nurses. The Gerontologist. 2019;59(2):327-37.
- Karasar N. Bilimsel Araştırma Yöntemi, Nobel Yayınevi 14. Baskı, Ankara. 2005:81-3.
- Şencan H. Sosyal ve Davranışsal Ölçümlerde Güvenirlik ve Geçerlilik. 1. ed. Ankara: Seçkin Yayınevi 2005.
- Tavşancıl E. Ölçme ile ilgili temel kavramlar. Tutumların ölçülmesi ve SPSS ile veri analizi. 3. ed: Nobel Yayın Dağıtım; 2006.
- Milisen K, Cremers S, Foreman MD, Vandevelde E, Haspeslagh M, De Geest S, et al. The strain of care for Delirium Index: a new instrument to assess nurses’ strain in caring for patients with delirium. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2004;41(7):775-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.03.005.
- Polit DF, Beck CT. The content validity index: are you sure you know what's being reported? Critique and recommendations. Research in nursing & health. 2006;29(5):489-97.
- Gürbüz S, Şahin F. Sosyal Bilimlerde Araştırma Yöntemleri Felsefe-Yöntem-Analiz. 4. ed: Seçkin Yayınevi.; 2017.
- Kalaycı S. SPSS uygulamalı çok değişkenli istatistik teknikleri. 5. ed: Asil Yayın Dağıtım Ltd. Şti.; 2010.
- Tavşancıl E. Tutumların ölçülmesi ve SPSS ile veri analizi. Ankara: Nobel Yayın Dağıtım; 2010.
- Polit DF, Beck CT. Essentials of nursing research:Appraising evidence for nursing practice. 7 ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.; 2010.
- Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS. Using Multivariate Statistics. Rotation. Oblique Rotation. . 6. ed. USA: Pearson Education Limited; 2014. 491,2,501. p.
- Çapık C, Gözüm S, Aksayan S. Kültürlerarası ölçek uyarlama aşamaları, dil ve kültür uyarlaması: Güncellenmiş rehber. Florence Nightingale Journal of Nursing. 2018;26(3):199-210. https://doi.org/10.26650/FNJN397481.
- Yurdugül H. Ölçek geliştirme çalışmalarında kapsam geçerlik indeksinin kullanımı. 2012.
- Yusoff MSB. ABC of content validation and content validity index calculation. Resource. 2019;11(2):49-54. https://doi.org/10.21315/eimj2019.11.2.6
- Doğan İ, Doğan N. Ölçek Geliştirme Çalışmalarında Kullanılan İçerik Geçerliliğine Genel Bir Bakış. Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Biostatistics. 2019;11(2).
- Uyumaz G, Dirlik EM, Çokluk Ö. AÇIMLAYICI FAKTÖR ANALİZİNDE TEKRAR EDİLEBİLİRLİK: KAVRAM VE UYGULAMA. Abant İzzet Baysal Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi. 2016;16(2):659-75.
- Aytaç M, Öngen B. Doğrulayıcı faktör analizi ile yeni çevresel paradigma ölçeğinin yapı geçerliliğinin incelenmesi. İstatistikçiler Dergisi: İstatistik ve Aktüerya. 2012;5(1):14-22.
- ÇAPIK C. Geçerlik ve güvenirlik çalişmalarinda doğrulayici faktör analizinin kullanimi. Anadolu Hemşirelik ve Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi. 2014;17(3):196-205.
- Evci N, Aylar F. Derleme: Ölçek geliştirme çalışmalarında doğrulayıcı faktör analizinin kullanımı. Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi. 2017;4(10):389-412.
- Hooper D, Coughlan J, Mullen MR. Structural equation modelling: Guidelines for determining model fit. Electronic journal of business research methods. 2008;6(1):pp53‑60-pp53‑60.
- Erkorkmaz Ü, Etikan İ, Demir O, Özdamar K, Sanisoğlu SY. Doğrulayıcı faktör analizi ve uyum indeksleri. Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013;33(1):210-23.
- Schubert A-L, Hagemann D, Voss A, Bergmann K. Evaluating the model fit of diffusion models with the root mean square error of approximation. Journal of Mathematical Psychology. 2017;77:29-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmp.2016.08.004
- Wang K, Xu Y, Wang C, Tan M, Chen P. A corrected goodness-of-fit index (CGFI) for model evaluation in structural equation modeling. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal. 2020;27(5):735-49. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10705511.2019.1695213 (accessed:13.09.2022).
- Gözüm S, Aksayan S. Kültürlerarası Ölçek Uyarlaması için Rehber II: Psikometrik Özellikler ve Kültürlerarası Karşılaştırma. Hemşirelikte Araştırma Geliştirme Dergisi 2003(5(1)):3-14.
- Shou Y, Sellbom M, Chen H-F. Fundamentals of Measurement in Clinical Psychology. Journal: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818697-8.00110-2 .
Copyright and license
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited.