Abstract
Objective:
The estimation of disease severity based on early biomarkers may facilitate treatment and reduce mortality in patients with COVID-19. The present retrospective, observational study evaluates the role of different inflammatory indices in predicting mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Materials and Methods:
The prognostic value for the prediction of 30-day mortality of inflammatory parameters [C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, procalcitonin (PCT)] and [neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), derived NLR (dNLR), systemic inflammation index (SII), C-reactive protein-to-lymphocyte ratio (CRP/L), C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio, and neutrophi-lto-lymphocyte and platelet ratio (N/LP)] were evaluated upon the initial admission of 305 COVID-19 patients to the intensive care unit.
Results:
In this study, APACHE score, ferritin, PCT and CRP/L were significantly higher in the non-survivors than in survivors. No significant differences were found in the other inflammatory indices. High ferritin (p<0.001) and high APACHE scores (p<0.001) were identified as predictors of in-hospital mortality in a ROC curve analysis. Only a high ferritin level was identified as an independent risk factor for mortality in a multivariate regression analysis (p=0.002).
Conclusion:
Inflammatory indices were not identified as predictors of mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients admitted to the intensive care unit in the present study; and only high ferritin levels among the parameters related to inflammation were identified as an independent risk factor for mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19, biomarker, inflammatory indices, ferritin, mortality
Introduction
The first case of Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) was reported in the city of Wuhan (Hubei, China), which walter named COVID-19 by the World Health Organization. It is a contagious disease that continues to threatenglobal public health. The causative agent is referred to as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) because of its similarity with SARS-CoV (1).
COVID-19 manifests with mild symptoms in most patients, although a considerable number of patients suffer from severe rapidly progressing pneumonia leading to multi-organ failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), septic shock, and death (2). It is important to identify prognostic factors for reducing COVID-19-related mortality in high-risk patients who are followed up in the intensive care unit (ICU). There remains a need for clinical studies on this subject (3-5).
Accumulating evidence in the literature suggests that an increased inflammatory response is responsible for fatal complications in critically ill patients with COVID-19 (3). Hyperinflammation plays an important role in viral pathogenesis. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction occurs as a result of hyperinflammatory response and severe cytokine stormleadsto multi-organ failure and death in patients (6). Significant increases in the levels of serum ferritin, procalcitonin, C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6, and other acute phase reactants are associated with mortality and prognosis in patients with COVID-19 (6).
The peripheral white blood cell count (WBC) and differential WBC counts (neutrophil, lymphocyte, platelet, monocyte) obtained by complete blood count (CBC) can be considered good biomarkers of systemic inflammatory response in critically ill patients. In recent studies in the literature, various inflammatory indices [i.e., neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte-monocyte ratio LMR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), derived NLR (dNLR), systemic inflammation index (SII), aggregate Index of systemic inflammation (AISI), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) and CPR/lymphocyte ratio (CRP/L)] have been investigated for their use as predictors of poor prognosis in patients with COVID-19, although these studies have yielded inconsistent results regarding the relationship between these biomarkers and prognosis (7). It is hypothesized in the present study that all these indices could serve as independent predictors of prognosis in patients with COVID-19. Thus, the present study evaluated the value of inflammatory indices and parameters for predicting prognosis in critically ill patients with COVID-19.
Materials and Methods
Ethical Statement
The study was conducted in the tertiary ICU of Yozgat City Hospital between May 2020 and May 2021. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Yozgat Bozok University (protocol number: 2017-KAEK-189_2021.09.27_03) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Study Design
For this single-center retrospective study, clinical, demographic, and laboratory data were retrieved from the hospital’s information management system and patient charts.
The study included adult ICU patients aged 18 years and older with a positive polymerase chain reaction test for COVID-19. After reviewing the patients’ records, we excluded those with hematological disorders, those with a history of severe liver disease and malignancy, those younger than 18 years of age, and those with missing laboratory data were excluded from the study.
Study Participants
The age, sex, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE 2) score, comorbidities, length of ICU stay, 30-day ICU mortality, need for mechanical ventilation in the first 24 hours, and need for inotropic support and renal placement therapy while in the ICU were recorded. Patients requiring mechanical ventilator support were defined as those undergoing resuscitation and endotracheal intubation due to cardiac or respiratory arrest. Patients were evaluated in two groups: Survivors (dischargedto home or transfer to the ward) and non-survivors (death during the ICU stay). The laboratory parameters measured upon admission to the ICU, including CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, WBC, differential neutrophil, platelet, and lymphocyte counts, and mean platelet volume, were retrieved from the hospital’s information management system.
Laboratory Measurements
The laboratory parameters measured in each patient from the venous blood samples collected upon admission to the ICU were retrieved from the hospital’s information management system. Inflammatory indices were calculated using CBC parameters as follows:
• SII= (neutrophil count×platelet count)/lymphocyte count;
• dNLR= neutrophil count/(WBC-neutrophil count);
• NLPR= (neutrophil count/lymphocyte count)×platelet count;
• CRP/albumin ratio= CRP/albumin, CRP/L=CRP/lymphocyte count;
• PLR= platelet/lymphocyte.
Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics Standard Concurrent User V 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY USA). Categorical data are presented in n and frequency, whereas continuous data were presented in mean ± standard deviation and median [interquartile range (IQR): 25th-75th percentile]. The normality of distribution was checked using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and histograms. The significance of differences between groups in terms of averages was assessed using the chi-square test, independent samples t-test, and Mann-Whitney U test. In cross tables, Fisher’s exact test was performed if more than 20% of the expected values were less than 5 or at least one of the values was less than 2. All significant variables were included in the multivariate logistic analysis after the univariate analysis. The factors predicting the mortality of patients with COVID-19 were investigated using a backward stepwise multivariate logistic regression analysis. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test for goodness-of-fit statistics was used to determine the calibration validation and discrimination of this regression analysis. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine the parameters that had the greatest predictive value for the mortality of patients with COVID-19, and the areas under the curve (AUC) were calculated.
Results
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
A total of 305 patients with COVID-19 (184 male; 121 female) were included in the study (Table 1). The median age was 72 years (IQR: 65-80 years). Of the total, 88 patients (28.9%) were discharged (survivors), and the remaining 217 patients (71.1%) died (non-survivors). Comorbidities included hypertension (48.2%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (31.5%), and coronary artery disease (25.6%). The median length of ICU stay was 9 days (IQR: 4-15 days).
| Table 1. Comparison of demographic and clinical characteristics of survivors and non-survivors | ||||
|
Variables |
Overall (n=305) |
Non-survivors (n=217) |
Survivors (n=88) |
p-value |
|
Age (years) |
72 [65 to 80] |
73 [66 to 81] |
71.5 [59.5 to 79] |
0.560 |
|
APACHE score |
23 [17 to 35] |
27 [18 to 37] |
19 [14 to 27] |
0.000 |
|
Length of ICU stay (days) |
9 [4 to 15] |
10 [5 to 17] |
7.5 [4 to 10] |
0.002 |
|
Sex, female/male |
121/184 (39.7/60.3) |
79/138 (36.4/63.6) |
42/46 (47.7/52.3) |
0.067# |
|
Comorbidities, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
147 (48.2) |
106 (48.8) |
41 (46.6) |
0.721# |
|
CHF |
39 (12.8) |
26 (12.0) |
13 (14.8) |
0.647* |
|
Diabetes mellitus |
55 (18.0) |
40 (18.4) |
15 (17.0) |
0.903* |
|
Neurologic disease |
54 (17.7) |
40 (18.4) |
14 (15.9) |
0.721* |
|
Arrhythmia |
20 (6.6) |
15 (6.9) |
5 (5.7) |
0.890* |
|
CAD |
78 (25.6) |
57 (26.3) |
21 (23.9) |
0.771* |
|
CKD |
72 (23.6) |
62 (28.6) |
10 (11.4) |
0.002* |
|
COPD |
96 (31.5) |
60 (27.6) |
36 (40.9) |
0.024# |
|
Other |
75 (24.7) |
57 (26.4) |
18 (20.5) |
0.346* |
|
Need for MV in the first 24 hours |
244 (80.0) |
195 (89.9) |
49 (55.7) |
<0.001* |
|
Need for vasoactive agent |
45 (14.8) |
42 (19.4) |
3 (3.4) |
0.001* |
|
Renal replacement therapy |
102 (33.6) |
83 (38.2) |
19 (21.8) |
0.006# |
| Data are presented as medians [interquartile range] for continuous variables and as numbers and percentages for categorical variables. Continuous variables were compared with a Mann-Whitney U test. Compared by the #: chi-square test and Yates’s correction for continuity. The level of statistical significance was set at 0.05. All statistically significant values are indicated in bold.APACHE: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation, ICU: intensive care unit, CHF: chronic heart failure, CAD: coronary artery disease, CKD: chronic kidney disease, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, MV: mechanical ventilation | ||||
As shown in Table 1, the APACHE score (27, IQR: 18-37 vs. 19, IQR: 14-27; p<0.001) was significantly higher, and the length of ICU stay was longer (median: 10.0 days, IQR: 5-17 days vs. 7.5 days, IQR: 4-10 days; p=0.002), chronic kidney disease (79% vs. 51%, p=0.002) was more common, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease was less common (27.6% vs. 40.9%, p=0.024) in the non-survivors than in the survivors. The need for mechanical ventilation in the first 24 hours (89.9% vs. 57.7%, p<0.001), the need for vasoactive agents (19.4% vs. 3.4%, p=0.001), and the need for renal replacement therapy (38.2% vs. 21.8%, p=0.006) were higher in the non-survivors than in the survivors.
Laboratory Parameters and Inflammatory Indices
An analysis of the laboratory parameters revealed (Table 2) significantly higher ferritin (median: 458; IQR: 237-787 vs. 257, IQR: 125.5-506; p<0.001) and PCT (median: 0.44; IQR: 0.13-1.68 vs. 0.175 IQR: 0.09-0.52, p<0.001) values among the inflammatory parameters; significantly higher urea (median: 63; IQR: 44-106 vs. 52 IQR: 33.5-80, p=0.003) and creatinine (median: 1.17; IQR: 0.87-1.83 vs. 0.99 IQR: 0.76-1.21, p=0.001) values among the biochemical parameters; and significantly higher CRP/L (median: 19.75; IQR: 8.30-44.50 vs. 13.3 IQR: 3.7-30.2, p=0.028) values among the inflammatory indices in the non-survivors than in the survivors. On the other hand, there were no significant differences in the CRP, albumin, and CBC parameters and other (SII, NLR, dNLR, NLPR, CRP/Alb, CRP/L, PRL,) inflammatory indices between the survivors and non-survivors (Table 2).
| Table 2. Comparison of laboratory variables between survivors and non-survivors | ||||
|
Variables |
Overall (n=305) |
Non-survivors (n=217) |
Survivors (n=88) |
p-value |
|
Inflammatory parameters |
||||
|
CRP (mg/dL) |
11.2 [7.01 to 21.5] |
11.6 [7.29 to 22.7] |
10.2 [3.95 to 18.9] |
0.053 |
|
Ferritin (ng/dL) |
413 [182 to 709] |
458 [237 to 787] |
257 [125.5 to 506] |
<0.001 |
|
PCT (ng/mL) |
0.35 [0.12 to 1.21] |
0.44 [0.13 to 1.68] |
0.175 [0.09 to 0.52] |
<0.001 |
|
Biochemical parameters |
||||
|
Urea (mg/dL) |
60 [42 to 93] |
63 [44 to 106] |
52 [33.5 to 80] |
0.003 |
|
Creatinine (mg/dL) |
1.09 [0.83 to 1.59] |
1.17 [0.87 to 1.83] |
0.99 [0.76 to 1.21] |
0.001 |
|
Albumin (g/dL) |
3.19 (0.48) |
3.17 (0.44) |
3.24 (0.56) |
0.293† |
|
Complete blood count |
||||
|
WBC (×109 L) |
8.6 [6.1 to 12.9] |
8.4 [6.2 to 12.7] |
9.05 [6.1 to 13.3] |
0.850 |
|
Neutrophils (×109 L) |
7.5 [4.7 to 11.6] |
7.4 [4.8 to 11.3] |
7.8 [4.3 to 11.9] |
0.925 |
|
Lymphocytes (×109 L) |
0.7 [0.4 to 1] |
0.7 [0.4 to 1] |
0.8 [0.45 to 1.1] |
0.076 |
|
Platelets (×109 L) |
202 [154 to 271] |
200 [149 to 259] |
209 [165 to 281.5] |
0.134 |
|
MPV (fL) |
8.4 [7.8 to 9.1] |
8.4 [7.9 to 9.1] |
8.4 [7.75 to 9.1] |
0.922 |
|
Inflammatory indices |
||||
|
SII |
2079.75 [938 to 4566] |
2120 [1001 to 4442] |
2063 [899 to 4942] |
0.879 |
|
NLR |
10.8 [5.5 to 19.3] |
10.8 [5.8 to 19.2] |
9.56 [4.54 to 21.25] |
0.328 |
|
dNLR |
5.66 [3.35 to 10.33] |
5.66 [3.4 to 10.42] |
5.02 [2.84 to 10.1] |
0.222 |
|
NLPR |
5.08 [2.90 to 10.40] |
5.16 [3.13 to 10.58] |
4.71 [2.46 to 9.22] |
0.139 |
|
CRP/alb |
3.55 [2.03 to 7.08] |
3.8 [2.2 to 7.5] |
3.17 [1.12 to 6.22] |
0.058 |
|
CRP/L |
16.66 [6.95 to 41] |
19.75 [8.30 to 44.66] |
13.3 [3.7 to 30.2] |
0.028 |
|
PLR |
290 [174 to 503] |
300 [180 to 498] |
253.35 [163 to 540] |
0.693 |
| Values are quoted as mean (standard deviation) and median [interquartile range]. †: Compared by independent sample t-test. Other values were compared with a Mann-Whitney U test. The level of statistical significance was set at 0.05. All statistically significant values are indicated in bold.CRP: C-reactive protein, PCT: procalcitonin, WBC: white blood cell, MPV: mean platelet volume, SII: systemic immune-inflammation index, NLR: neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, dNLR: derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, NLPR: neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, platelet ratio, CRP/alb: C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio, CRP/L: C-reactive protein-to-lymphocyte ratio, PLR: platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | ||||
Predictive Accuracy of Laboratory Parameters for Mortality
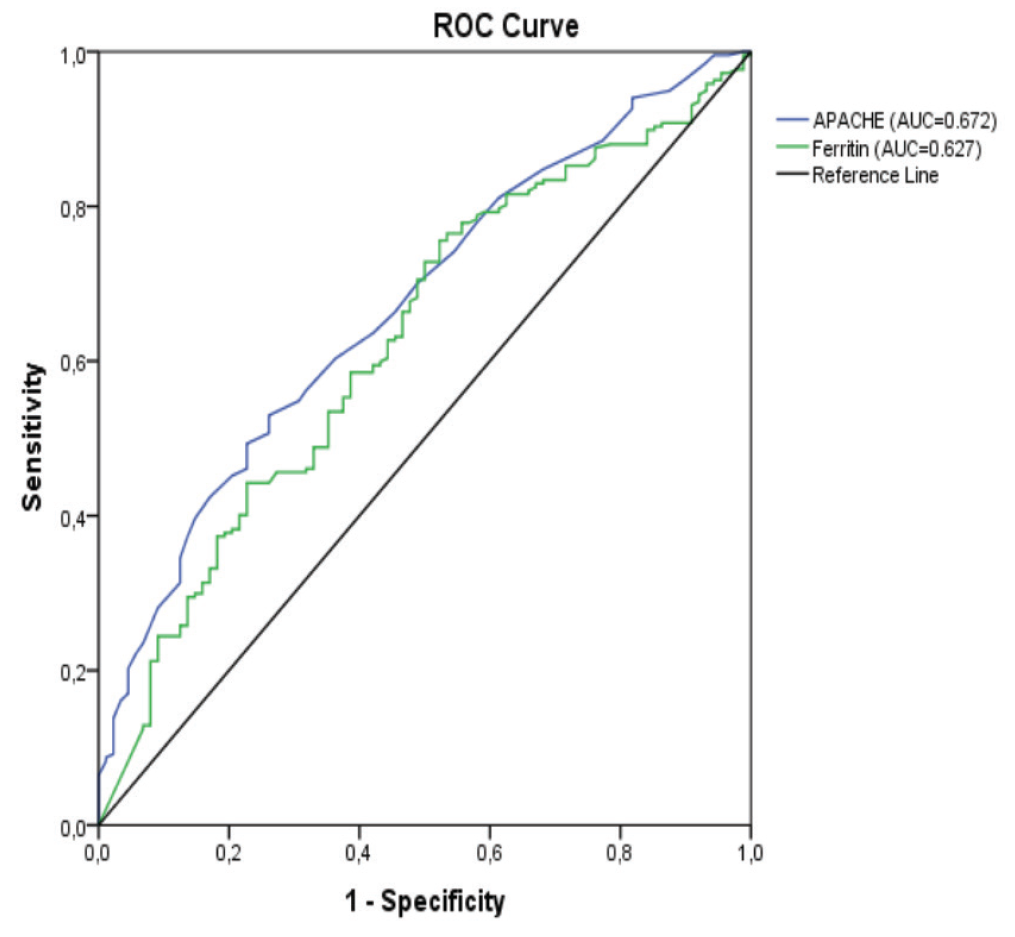
In the ROC curve analysis for mortality in patients with COVID-19, the optimal cut-off value was 19.5 [AUC=0.672, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.607-0.736, p<0.001] for the APACHE score and 263.0 ng/dL (AUC=0.627, 95% CI 0.559-0.696, p<0.001) for ferritin (Table 3). Among the other inflammatory parameters, the ROC curve analysis for CRP/L did not reveal a significant level for the prediction of mortality in patients with COVID-19 (p<0.05).
| Table 3. ROC curve analysis predicting the mortality of COVID-19 patients | |||||||
|
Variables |
AUC |
Cut-off point |
Sensitivity (%) |
Specificity (%) |
p-value |
95% CI |
|
|
Lower |
Upper |
||||||
|
APACHE score |
0.672 |
19.5 |
70.0 |
51.1 |
<0.001 |
0.607 |
0.736 |
|
Ferritin |
0.627 |
263.0 |
71.0 |
50.0 |
<0.001 |
0.559 |
0.696 |
| The level of statistical significance was set at 0.05. All statistically significant values are indicated in bold.AUC: Area under the curve, APACHE: acute physiology and chronic health evaluation, CI: confidence interval, COVID-19: coronavirus disease-2019, ROC: receiver operating characteristic | |||||||
Risk Factors for COVID-19 Mortality in Univariate and Multivariate Analyses
The ICU mortality rate in the entire study population was 71.1%. The results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses for mortality among patients with COVID-19 are presented in Table 4.
| Table 4. Univariate and multivariate analysis for the mortality of COVID-19 patients | ||||||
|
Variables |
Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
||||
|
OR |
(95% CI) |
p-value |
OR |
(95% CI) |
p-value |
|
|
APACHE score |
0.944 |
(0.921-0.964) |
<0.001 |
0.947 |
(0.923-0.972) |
<0.001 |
|
CRP |
0.978 |
(0.955-1.001) |
0.066 |
|
|
|
|
Ferritin |
0.999 |
(0.998-1.000) |
0.002 |
0.999 |
(0.998-1.000) |
0.002 |
|
PCT |
0.963 |
(0.917-1.012) |
0.140 |
|
|
|
|
Urea |
0.992 |
(0.986-0.998) |
0.007 |
0.996 |
(0.990-1.002) |
0.196 |
|
Creatinine |
0.671 |
(0.499-0.903) |
0.008 |
|
|
|
|
CRP/L |
0.993 |
(0.985-1.001) |
0.098 |
|
|
|
| Multivariate Model’s Adjusted R2=0.183, p-value <0.001.The level of statistical significance was set at 0.05. All statistically significant values are indicated in bold.APACHE: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation, CRP: C-reactive protein, CRP/L: CRP-to-lymphocyte ratio, CI: confidence interval, PCT: procalcitonin, OR: odds ratio, COVID-19: coronavirus disease-2019 | ||||||
In the univariate analysis, the APACHE score, ferritin, urea, and creatinine were identified as significant predictors of mortality, whereasin the multivariate analysis, high ferritin levels [odds ratio (OR)=0.999; 95% CI 0.998-1.000; p=0.002] and APACHE score (OR=0.947; 95% CI 0.923-0.972; p<0.001) were identified as independent predictors of mortality (Figure 1).
Discussion
The present study evaluating the relationship between inflammatory indices, based on the laboratory parameters measured upon initial admission, and mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients has produced several important results. Ferritin, urea, and creatinine levels were higher in the non-survivors than in the survivors. Among the inflammatory indices, CRP/L was higher in the non-survivors. High ferritin levels and APACHE scores were independent predictors of mortality.
Predicting prognosis is of utmost importance in critically ill patients with COVID-19 who have a high mortality rate. Clinical studies have generally reported decreased T lymphocyte and CD3, CD4, and CD8 levels together with an increase in proinflammatory cytokines. Cytokine storms have been linked to disease severity, leading to multi-organ failure and death (8). In such cases, the increase in the number of inflammatory cells at the level of the endothelium is known to impair microcirculation and to cause systemic impairment in different organs in COVID-19 patients (6). Further studies have reported various laboratory abnormalities in response to an exaggerated inflammatory response in critically ill patients with COVID-19 (9, 10), and these resultsresults are important indicators of systemic inflammation and immune response (9, 11). Many studies have evaluated the relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and poor outcomes in patients with COVID-19 (10-13). The present study aimed to analyze the predictive value of inflammatory indices derived from inflammatory markers on mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19 who exhibit an exaggerated immune response.
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, a significant increase in CRP concentrations was most frequently attributed to a condition caused by a bacterial pathogen (14). However, elevated CRP levels have also been reported in severe viral infections, including pneumonia caused by H1N1 influenza, and particularly in COVID-19 patients in recent years (15, 16). Furthermore, as a biomarker of inflammation, CRP is strongly linked to disease severity, ARDS, and mortality in such patients (17). Yang et al. (18) reported CRP/L as a highly sensitive indicator of disease severity in patients with early COVID-19 pneumonia, and while similar to the present study, they reported a higher CRP/L ratio in non-survivors, CRP/L did not predict mortality in a univariate regression analysis. In contrast to the findings of the present study, Ullah et al. (19) reported the lymphocyte-to-CRP ratio (LCR) to be a sensitive predictor of the inflammatory cascade and should be considered as a potential new predictor of in-hospital mortality and poor outcomes in patients with COVID-19. The same study reported an association between an increased risk of in-hospital mortality and low LCR (19). In another study, Acar et al. (20) reported that LCR was a significant independent predictor of in-hospital mortality in 148 patients. LCR has high sensitivity in the acute phase of inflammation because CRP levels increase early before the emergence of neutrophilia or lymphopenia, regardless of the reasons for the elevated levels (i.e., infections, cancer, autoimmune) (19). For this reason, elevated LCR may be regarded as an independent biomarker of the initial stages of inflammation. Although it is well established that the NLR correlates with the severity of COVID-19, it is important to know that the NLR can be affected in immunosuppressed patients or in those receiving high-dose corticosteroid therapy (21). For this reason, the authors believe the low CLR is attributable to the fact that all patients were initiated on corticosteroid therapy upon admission to the ICU.
Ferritin, an inflammatory parameter, plays an important role in mortality in patients with COVID-19. Lucijanic et al. (22) reported that elevated ferritin levels were associated with poorer prognosis and death in patients with COVID-19 than in those with low ferritin levels. In their study, Hou et al. (23) suggested the use of ferritin as a predictor of disease severity in critically ill COVID-19 patients based on their multivariate logistic regression analysis (23), whereas Cecconi et al. (24) reported that ferritin could be useful for the early identification of a risk of deterioration in the clinical condition of hospitalized COVID-19 patients that may result in transfer to the ICU or death, and in the determination of the treatment approach. Elevated ferritin levels, a marker of inflammation, have been associated with increased mortality considering their contribution to the development of both cytokine storms and ARDS (25). Consistent with these studies, the multivariate logistic regression analysis in the present study found that only elevated ferritin levels could serve as an independent indicator of mortality.
Under normal circumstances, procalcitonin is produced and released into circulation by the parafollicular C-cells in the thyroid gland, and is produced in substantial quantities in extrathyroidal tissues during severe infections (26) and maintained by increased interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α and IL-6 concentrations. Procalcitonin has been reported to better differentiate between bacterial infections and other inflammatory processes than WBC count and CRP (27). Although Lippi and Plebani (28) found that bacterial co-infection resulted in elevated procalcitonin levels, Kotula et al. (29) reported elevated procalcitonin levels in patients with confirmed viral infection but without bacterial infection. In another study, higher procalcitonin levels were identified in critically ill COVID-19 patients than in those without critical illness (30). Similarly, procalcitonin levels were significantly higher in non-survivors than in survivors. In a meta-analysis of four studies, Lippi and Plebani (28) reported that serial procalcitonin measurement was useful for predicting prognosis in patients with COVID-19. The authors of the present study believe that although COVID-19 is a viral infection, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PTC) measurement could be useful in predicting prognosis and could support treatment decisions in patients with COVID-19.
There are several studies in the literature investigating the relationship between various inflammatory indices and prognosis and mortality in COVID-19. Ding et al. (31) reported a significant relationship between NLR after the fifth day of hospital admission and the length of hospital stay in 72 patients with COVID-19 and suggested that NLR measured after the fifth day of hospitalization could be used to predict prognosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Seyit et al. (32) reported that PRL upon initial admission to the emergency room showed a better correlation with disease severity than NLR in 110 COVID-19 patients (32). When the findings of the present study are examined in detail, inflammatory indices, such as NLR, PLR, dNLR, SII, CRP/alb, and NPLR, which are known to predict prognosis in patients with COVID-19, were found to be unrelated to mortality.
In a study of 114 patients with COVID-19, Xue et al. (33) reported that NLR, PLR, dNLR, and SII, measured at the time of admission to the hospital, were insufficient for predicting disease severity, although they did not evaluate mortality rates. Similarly, in a study evaluating the SII measured from blood tests performed within 1 hour of hospitalization in 285 patients, Kudlinski et al. (34) identified no significant value of the SII in predicting mortality.
In addition, Ullah et al. (19) compared LCR and NLR in terms of their performance in predicting in-hospital mortality in the early period and found that NLR could significantly predict mortality and the need for mechanical ventilation on day 7, whereas NLR measured on day 1 had no significant predictive power. They also reported that the values may vary, with the potential to be increased in those receiving steroid therapy and decreased in those with bone marrow suppression due to cancer or chemotherapy (19). The authors of the present study believe that the inflammatory indices of the study patients may have been affected considering that all critically ill patients requiring oxygen supplementation due to respiratory distress, unless contraindicated, received dexamethasone 6 mg/day, prednisolone 0.5-1 mg/kg, or its equivalent methylprednisolone for 10 days, as per the treatment guidelines published by the Ministry of Health of Turkey (35).
Study Limitations
The present study has some limitations, the first of which is its retrospective and single-center design. Multicenter studies will certainly contribute significantly to the literature. The second limitation is that the administration of steroid therapy to patients without contraindications, as per the treatment protocols, may have affected the inflammatory indices, although the studied inflammatory markers were comparable considering that these therapies have been standardized. The strengths of the present study include its sample of 305 ICU patients, and the ICU follow-up and treatment of these patients had been performed by the same team. An additional strength of the study to be considered is its simultaneous examination of multiple parameters in the same patient group, which have been evaluated in dispersed groups in previous studies.
Conclusion
In the present study, inflammatory indices were not identified as predictors of mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19 admitted to the ICU, and only high ferritin levels were identified as independent risk factors for mortality. Ferritin levels at the time of admission to the ICU can be useful for predicting prognosis in critically ill ICU patients, including those with COVID-19.
Ethics
Authorship Contributions
References
- Grasselli G, Zangrillo A, Zanella A, Antonelli M, Cabrini L, Castelli A, et al. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020;323:1574-81.
- van Eijk LE, Binkhorst M, Bourgonje AR, Offringa AK, Mulder DJ, Bos EM, et al. COVID-19: immunopathology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment options. J Pathol. 2021;254:307-31.
- Yang AP, Liu JP, Tao WQ, Li HM. The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106504.
- Doganci S, Ince ME, Ors N, Yildirim AK, Sir E, Karabacak K, et al. A new COVID-19 prediction scoring model for in-hospital mortality: experiences from Turkey, single center retrospective cohort analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24:10247-57.
- Usul E, Şan İ, Bekgöz B, Şahin A. Role of hematological parameters in COVID-19 patients in the emergency room. Biomark Med. 2020;14:1207-15.
- 6.Tomar B, Anders HJ, Desai J, Mulay SR. Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Drive Necroinflammation in COVID-19. Cells. 2020;9:1383.
- Karimi A, Shobeiri P, Kulasinghe A, Rezaei N. Novel Systemic Inflammation Markers to Predict COVID-19 Prognosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:741061.
- Fois AG, Paliogiannis P, Scano V, Cau S, Babudieri S, Perra R, et al. The Systemic Inflammation Index on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Molecules. 2020;25:5725.
- Rokni M, Ahmadikia K, Asghari S, Mashaei S, Hassanali F. Comparison of clinical, para-clinical and laboratory findings in survived and deceased patients with COVID-19: diagnostic role of inflammatory indications in determining the severity of illness. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20:869.
- Tjendra Y, Al Mana AF, Espejo AP, Akgun Y, Millan NC, Gomez-Fernandez C, et al. Predicting Disease Severity and Outcome in COVID-19 Patients: A Review of Multiple Biomarkers. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020;144:1465-74.
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507-13.
- Paliogiannis P, Zinellu A, Scano V, Mulas G, De Riu G, Pascale RM, et al. Laboratory test alterations in patients with COVID-19 and non COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia: a preliminary report. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2020;14:685-90.
- Gerotziafas GT, Sergentanis TN, Voiriot G, Lassel L, Papageorgiou C, Elabbadi A, et al. Derivation and Validation of a Predictive Score for Disease Worsening in Patients with COVID-19. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:1680-90.
- Vanderschueren S, Deeren D, Knockaert DC, Bobbaers H, Bossuyt X, Peetermans W. Extremely elevated C-reactive protein. Eur J Intern Med. 2006;17:430-3.
- Vasileva D, Badawi A. C-reactive protein as a biomarker of severe H1N1 influenza. Inflamm Res. 2019;68:39-46.
- Luo X, Zhou W, Yan X, Guo T, Wang B, Xia H, et al. Prognostic Value of C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Coronavirus 2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71:2174-9.
- Smilowitz NR, Kunichoff D, Garshick M, Shah B, Pillinger M, Hochman JS, et al. C-reactive protein and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:2270-9.
- Yang M, Chen X, Xu Y. A Retrospective Study of the C-Reactive Protein to Lymphocyte Ratio and Disease Severity in 108 Patients with Early COVID-19 Pneumonia from January to March 2020 in Wuhan, China. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e926393.
- Ullah W, Basyal B, Tariq S, Almas T, Saeed R, Roomi S, et al. Lymphocyte-to-C-Reactive Protein Ratio: A Novel Predictor of Adverse Outcomes in COVID-19. J Clin Med Res. 2020;12:415-22.
- Acar E, Demir A, Yıldırım B, Kaya MG, Gökçek K. The role of hemogram parameters and C-reactive protein in predicting mortality in COVID-19 infection. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75:e14256.
- Tonduangu N, Le Borgne P, Lefebvre F, Alame K, Bérard L, Gottwalles Y, et al. Prognostic Value of C-Reactive Protein to Lymphocyte Ratio (CLR) in Emergency Department Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J Pers Med. 2021;11:1274.
- Lucijanic M, Demaria M, Gnjidic J, Rob Z, Filipovic D, Penovic T, Jordan A, Barisic-Jaman M, Pastrović F, Lucijanic D, Cikara T, Lucijanic T, Miletic M, Ljubicic D, Keres T. Higher ferritin levels in COVID-19 patients are associated with hyperinflammation, worse prognosis, and more bacterial infections without pronounced features of hemophagocytosis. Ann Hematol. 2022 May;101(5):1119-1121.
- Hou H, Zhang B, Huang H, Luo Y, Wu S, Tang G, et al. Using IL-2R/lymphocytes for predicting the clinical progression of patients with COVID-19. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020;201:76-84.
- Cecconi M, Piovani D, Brunetta E, Aghemo A, Greco M, Ciccarelli M, et al. Early Predictors of Clinical Deterioration in a Cohort of 239 Patients Hospitalized for Covid-19 Infection in Lombardy, Italy. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1548.
- Para O, Caruso L, Pestelli G, Tangianu F, Carrara D, Maddaluni L, et al. Ferritin as prognostic marker in COVID-19: the FerVid study. Postgrad Med. 2022;134:58-63.
- Cleland DA, Eranki AP Procalcitonin. StatPearls; [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020. [cited: 2020 Apr 22]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539794/
- Ponti G, Maccaferri M, Ruini C, Tomasi A, Ozben T. Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2020;57:389-99.
- Lippi G, Plebani M. Procalcitonin in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;505:190-1.
- Kotula JJ, Moore WS, Chopra A, Cies JJ. Association of Procalcitonin Value and Bacterial Coinfections in Pediatric Patients With Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Admitted to the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2018;23:466-72.
- Zhang JJ, Dong X, Cao YY, Yuan YD, Yang YB, Yan YQ, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy. 2020;75:1730-41.
- Ding X, Yu Y, Lu B, Huo J, Chen M, Kang Y. Dynamic profile and clinical implications of hematological parameters in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020;58:1365-71.
- Seyit M, Avci E, Nar R, Senol H, Yilmaz A, Ozen M, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte to monocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio to predict the severity of COVID-19. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;40:110-4.
- Xue G, Gan X, Wu Z, Xie D, Xiong Y, Hua L, et al. Novel serological biomarkers for inflammation in predicting disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;89:107065.
- Kudlinski B, Zgoła D, Stolińska M, Murkos M, Kania J, Nowak P, et al. Systemic Inflammatory Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics. 2022;12:859.
- COVID-19 Rehberi [İnternet]. T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı COVID-19 Bilgilendirme Platformu. [erişim tarihi: 7 Kasım 2020]. Erişim adresi: https://covid19.saglik.gov.tr/TR-66341/antisitokin-antiinflamatuar-tedaviler-koagulopati-yonetimi.html
Copyright and license
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited.